by Fran McVeigh

The #G2Great chat was electrifying on 9/23/21 as the Twitterverse welcomed C.C. Bates, Maryann McBride, and Jan Richardson for their chat around their new book, The Next Step Forward in Running Records: Getting to the Heart of Effective Instruction Through Deeper Qualitative Analysis. Dr. Jan Richardson is no stranger to #G2Great as she hosted on July 28, 2016 for The Next Step Forward in Guided Reading. This new text has so much information about running records that it would be ideal for a study by partner teachers, teams of teachers, or even a full faculty building level study. In the educational world, C.C. Bates, Maryann McBride and Jan Richardson have a total of over 100 years of experience that they honed as they wrote this text and their wisdom is found on every page.
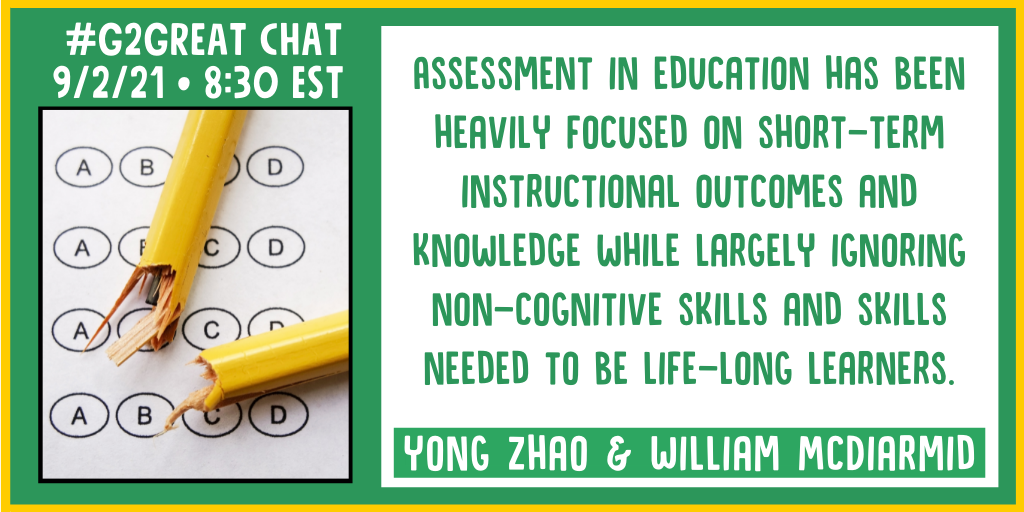
Many educators are totally stressed by the role of assessment in their lives as they try to survive and even hope to thrive during these pandemic times. So let’s begin this post with the authors’ response to WHY they wrote this book.
1) What motivated you to write this book? What impact did you hope that it would have in the professional world?
We felt running records were falling short of their potential. Often times we would see teachers calculate the accuracy rate and ignore the analysis of other behaviors including errors and self-corrections. We hoped the book would provide opportunities for professional conversations around how running records can be used to make instructional decisions. The book incorporates questions we have received from teachers nationwide. The book addresses these questions and provides guidance on why running records are important, how to take, score, and analyze them, and connect the analysis to individual, small, and whole group instruction. Finally, the book provides insight into specific challenges that are uncovered through a detailed analysis of running records.
Email correspondence with C.C. Bates, Maryann McBride, & Jan Richardson
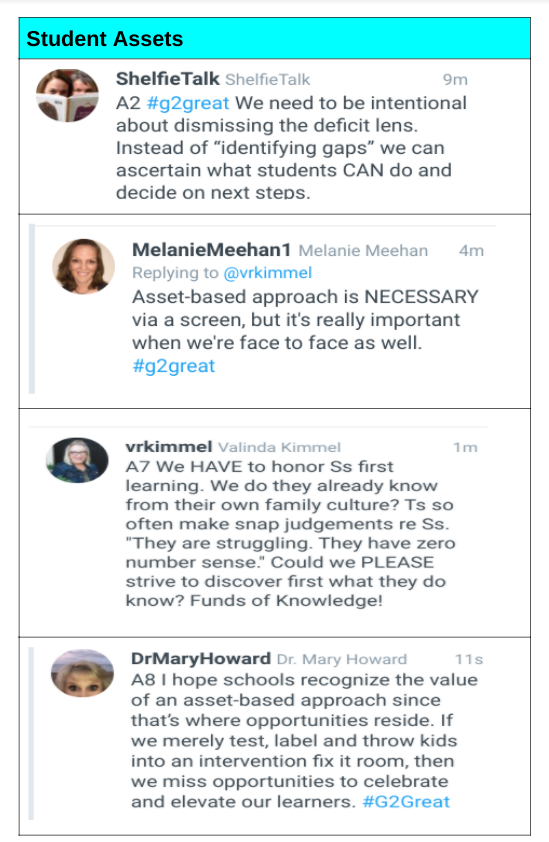
There is so much to consider when using Running Records. They are simplistic in design: a written response to what the student said out loud while reading. That “inside out” view of student processing. The deeper meaning comes from the qualitative analysis with the changes in instruction coming from a study of student patterns and teacher reflection on instruction over time. To hear that teachers would often only calculate the accuracy rate is disheartening.
I would be remiss to not state my own personal bias. Running records informed my life as a special education teacher, as a classroom teacher, as a curriculum coordinator, and as a literacy consultant. The information gained from running records analysis has the potential to transform instruction for students. The information gained from teacher analysis of their own TOLDs would be reflective action research that could also change a teacher’s self awareness. Running records are powerful in the hands of a thoughtful, reflective, research-oriented teacher.
Let us continue. This post is going to identify five key points about running records from The Next Step in Running Records that were amplified by the chat.
Know your purpose for running records
Running records would typically be classified as formative assessments. This process: take a running record, score, analyze, and then connect to individual, small and whole group instruction. All of this information is used to then guide the teacher’s decision making in developing an instructional plan that includes choosing a book for instruction, choosing the next steps in letter and word work, as well as the next steps in vocabulary, language and strategic action. Other decisions include the type of passage to be used: a cold passage (never read before) or a reread of a passage that the student has read once before.
MSV is not the order of importance
MSV is the alphabetical order of three areas. Let me repeat that. MSV is the alphabetical order of the three areas.
It is not the order of importance.
There is synergy in the crosschecking that occurs often almost simultaneously between these areas. V or Visual is a priority for “phonics instruction” because it deals with attending to the print that is in the text in front of the students. Letters. Sounds. Decoding the words. Visual information is about the print (not the illustrations). The print is often the first area that many teachers consider when they want to know if phonics instruction is working/ sticking. V or visual information is important and many critics of balanced reading instruction claim that “phonics is last in instruction” because visual is last one listed in MSV. But the listing of MSV is truly alphabetical order.
(Note: I spend a lot of time on analysis of the visual information processing to ensure that phonics instruction is meeting the needs of students.)
MSV is an analysis of student reading behaviors
Why analysis?
What are some of the the key student reading behaviors?
“V or visual information stands for the ways in which children draw upon the alphabetic principle or the connection between letters and sounds. V also includes children’s use of orthographic patterns and their automatic recognition of high-frequency words.” (p. 23) Visual information does NOT include pictures/photographs.
M is meaning and is a focus on constructing understanding whether at the paragraph, sentence, phrase, or word level. The author’s use the example of a child reading “The house is brown” for “The horse is brown” where it does make sense at the sentence level but not the text level if the child is reading about horses. We do want student using both visual and meaning simultaneously and these types of miscues can easily be clarified as words that need to be studied in the middle (/u/ and /r/) as the beginning and endings are correct.
S is structure and deals with the language and the grammar. Some miscues occur due to language or grammar that is unfamiliar to students. Coordinating the language and grammar with the visual information in the text is a challenge when the child is working with text that is outside their current areas of cognitive practice.
Monitoring and self-correcting are also windows into student processing. What the student says is important as they attempt to solve a word. Student work in their head and out loud provides data for teachers to analyze.
This was just an abbreviated overview of complex reading behaviors that are detailed in The Next Step Forward in Running Records. These behaviors can be accessed during every running record taken of a child’s reading. What a gift for teachers and students.
A running record is the key to developing a responsive instructional plan
Reading behaviors operate together. They may be analyzed separately as MSV or physical behaviors during the running record but the goal is for the behaviors to work together in order for student processing systems to function effectively. The goal of analysis is to determine which ones and HOW they are being used in order to plan for the next layer of instruction needed by the child. And inn the tweet below, C.C. Bates shares one example of what is NOT an instructional implication.
Pay attention to patterns of behavior that emerge over time
Don’t shortchange running records by just looking at accuracy. Look for patterns over time to inform and guide responsive differentiated instruction.
Let’s return to the words of the authors for a response to question two for takeaways for teachers to embrace and question three with a message from the heart.
2) What are your BIG takeaways from your book that you hope teachers will embrace in their teaching practices?
We hope teachers will see that capturing students’ reading behaviors and using the information to provide targeted instruction is time well spent. In the book, we show how running records are an integral part of the instructional cycle. We give suggestions on when to take running records, with whom, and how often. Most importantly we attempt to help teachers move beyond the accuracy rate to deepen their understanding of students’ literacy behaviors and their instructional implications.
Email correspondence with C.C. Bates, Maryann McBride, & Jan Richardson
3) What is a message from the heart you would like for every teacher to keep in mind?
This book was a pandemic project. Focusing our energy on a topic near and dear to our hearts kept us grounded and moving forward as we tried to balance our personal and professional lives. Running records do require time, energy, thought, but we believe that children are always worth the effort!
Email correspondence with C.C. Bates, Maryann McBride, & Jan Richardson
Closing thoughts . . .
Are you using running records? If yes, how and why do you use them? If no, why not?
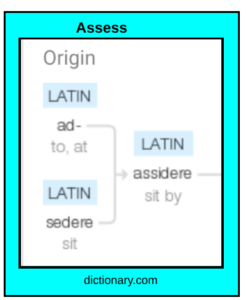
Any passage can be used for a running record that can be analyzed in order to determine the reading behaviors that students are consistently using as well as the next possible steps for instruction. Running records provide a window into a child’s brain to assess their reading behaviors. As a reminder, the word assess comes from the Latin assidere, which means to sit beside. Literally then, to assess means ‘to sit beside the learner.” A running record allows a child to sit beside an adult who listens intently to the child read and watches their reading behaviors. When I am taking a running record, I pull all that information together for analysis of those in-the-head behaviors along with the behaviors I observe during our work together. I believe it is important for an adult who understands the value of a deep analysis to listen to children to determine whether they are applying skills that they have been taught as they read connected text.
Isn’t that what every child in every classroom deserves?
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
LINKS:
https://vimeo.com/517580786 – Running Records Webinar by Jan, C.C., and Maryann
https://www.janrichardsonreading.com
https://readingrecovery.clemson.edu – Click on Teacher Resources for more on running records
Why do you need to read and study this book?
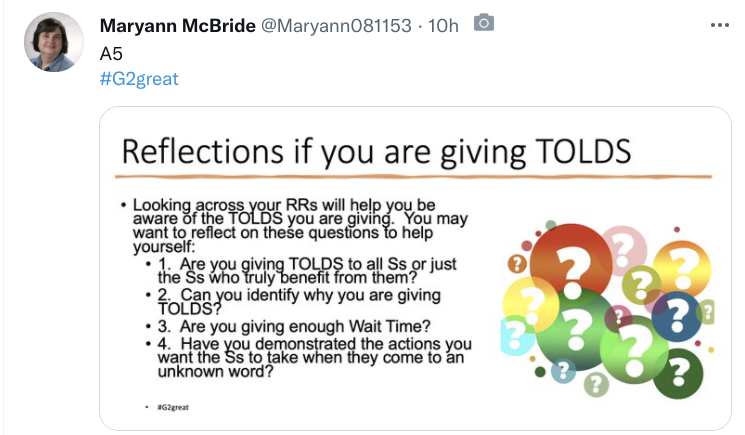
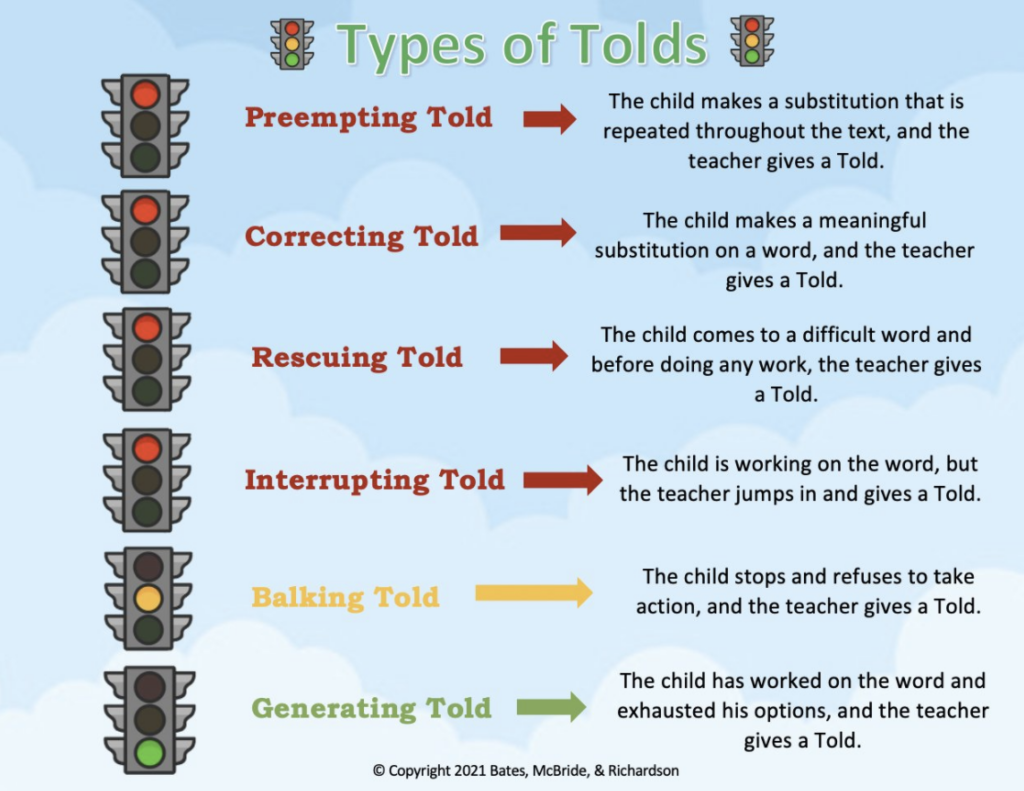
The book will help you understand the depth of the previous information as well as these Additional Tweets to Consider about TOLDS (a Teacher Behavior) that are an ENTIRE chapter in the book: